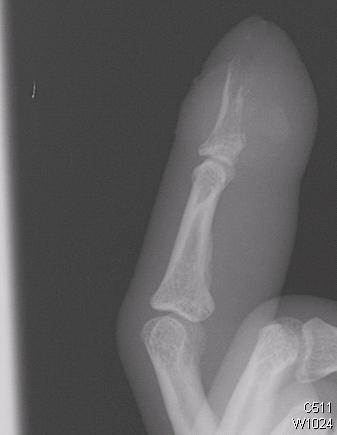
Bone Lesions Case 4 Diagnosis
Diagnosis: Osteomyelitis
Initial plain films may be negative, particularly in the first 7-10 days, since 30-50% of bone mineral must be lost for osteomyelitis to appear radiographically. 90% have abnormal X rays by 28 days. MRI and technetium bone scans can detect osteomyelitis in the first 48-72 hours.
Radiographic findings include:
- Lucent lytic areas of cortical bone destruction
- Involcrum (cloak of laminated/spiculated periosteal reaction, seen after 20 days)
- Sequestrum (detached cortical necrotic bone, seen after 30 days)
- Cloaca formation (space in which dead bone resides).
WBC count is nonspecific. ESR is sensitive but has poor specificity. One exception is patients with diabetic foot ulcers. An ESR of >100 is specific for osteomyelitis in these patients. CRP is less sensitive and more specific than ESR. It is abnormal within 24 hours of onset and should normalize within one week with proper treatment.
The gold standard for diagnosis is surgical biopsy. Culture from needle-guided biopsy is also acceptable. Swab cultures do not reliably match biopsy results and are unacceptable.