Leg/Knee Case 4 ED Management
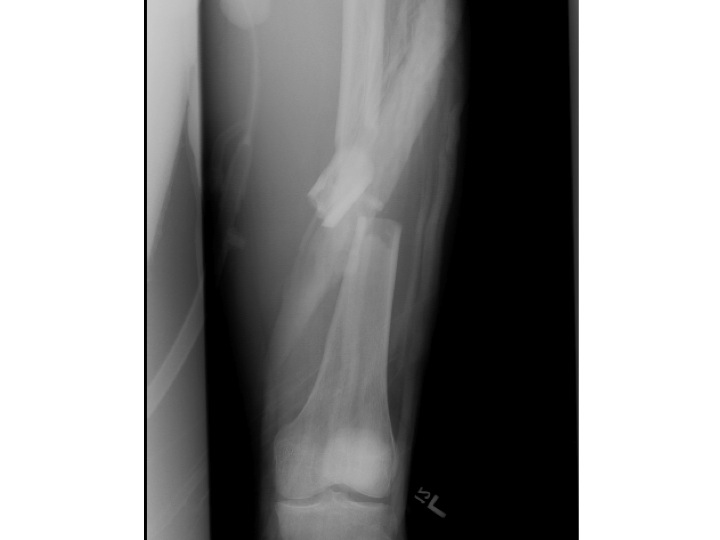
Femoral Shaft Fracture
ED Management
Initial management begins with trauma ABC's.
Preoperative labs and blood typing should be sent since many require transfusion.
Immediate orthopedic consultation is indicated. Immediate immobilization with Hare or Sager traction or a Thomas splint should be performed. However, traction is relatively contraindicated in the setting of open fractures or sciatic nerve injuries. According to one author, the goal is definitive surgical stabilization within 24 hours in stable patients. Initiate intravenous antibiotics and ensure tetanus immunizations are updated for open fractures.
Fat embolism, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism are serious complications, so patients should be monitored for hypoxia or increased respiratory effort.