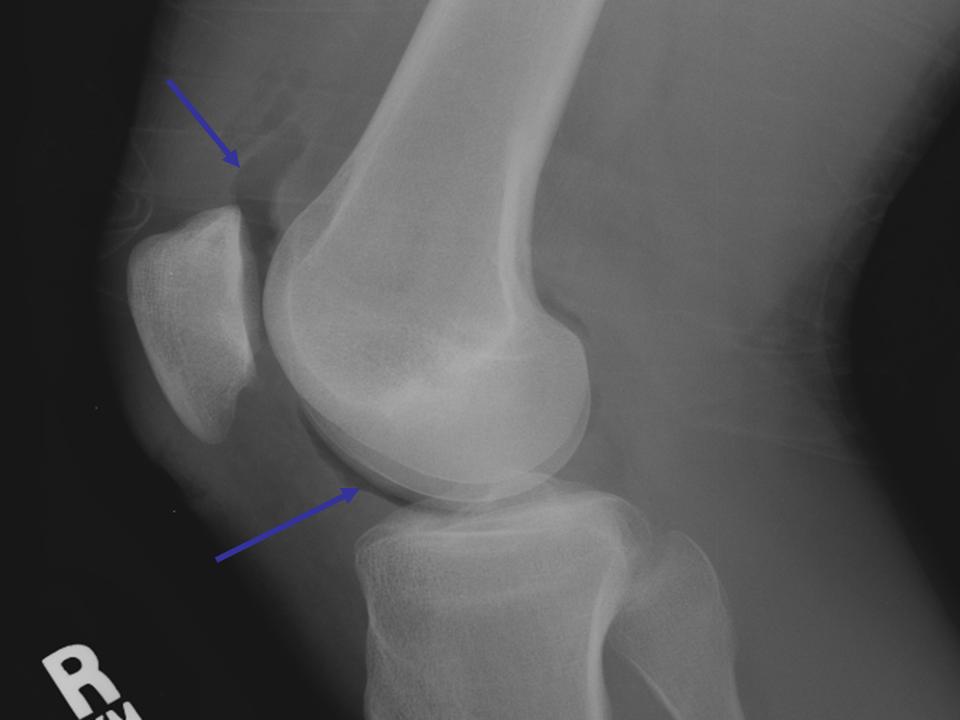
Soft Tissue Case 2 Diagnosis
Intraarticular wound (air in joint space)
Diagnosis
Air in the joint on plain radiographs confirms that the joint was penetrated. CT scan can also detect intraarticular air.
In the absence of air on plain films, patients with suspicious wounds should have a diagnostic arthrogram:
- Use a 30 ml syringe with an 18 gauge needle.
- Select a site for arthrocentesis away from the wound tract.
- Sterilly aspirate the joint. Blood return signifies hemarthrosis likely from intraarticular extension of the wound.
- If no blood is aspirated, inject normal saline with a few drops of sterile fluorescein or methylene blue until the joint is fully distended.
- Observe for extravasation of the dye from the wound, which would confirm intraarticular involvement.